深入瞭解 Referrer Policy
Response Header 也能設定 referrerPolicy?
上一篇談到使用 fetch API 的參數來設定 referrerPolicy,現在要來談談如何從 Server Side 去設定,使用 NodeJS HTTP module 來實作簡易的 HTTP server,設定 no-referrer,並且載入跨域的圖片跟影片
httpServer.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader("Referrer-Policy", "no-referrer");
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.end(`<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head></head>
<body>
<video src="https://youtu.be/79RLkH3T8hg?si=VcjfDcGujMj3ZXhU"></video>
<img src="https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png" />
</body>
</html>`);
});
我們用瀏覽器打開 http://localhost:5000/ > F12 > Network > General,觀察 Referrer Policy:
http://localhost:5000/ ,使用瀏覽器預設的 Referrer Policy: strict-origin-when-cross-origin 是合理的,因為請求這個資源時,還沒收到 Server 回傳的 response header,所以使用預設值
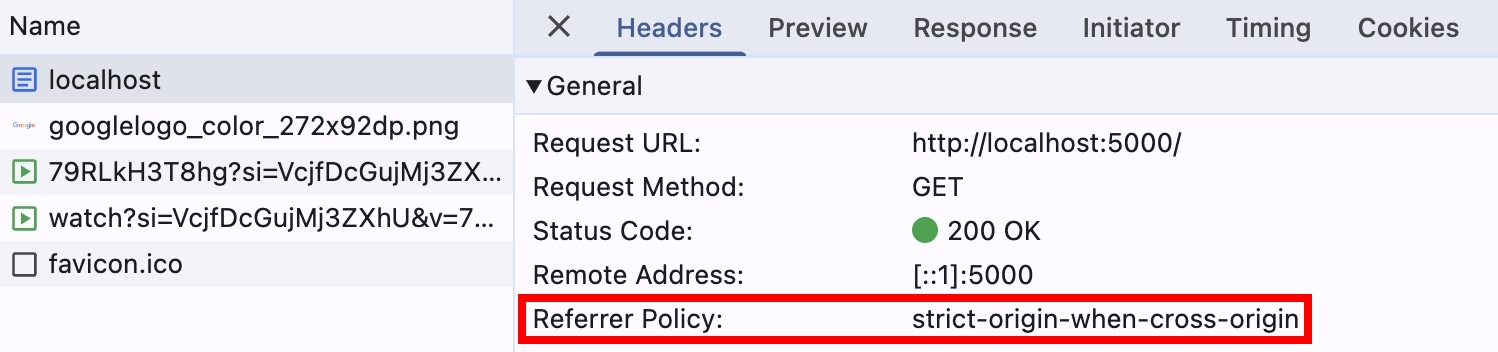
瀏覽器後續解析 HTML,並且請求跨域的圖片跟影片,此時就會套用 Server 回傳的 Referrer Policy: no-referrer
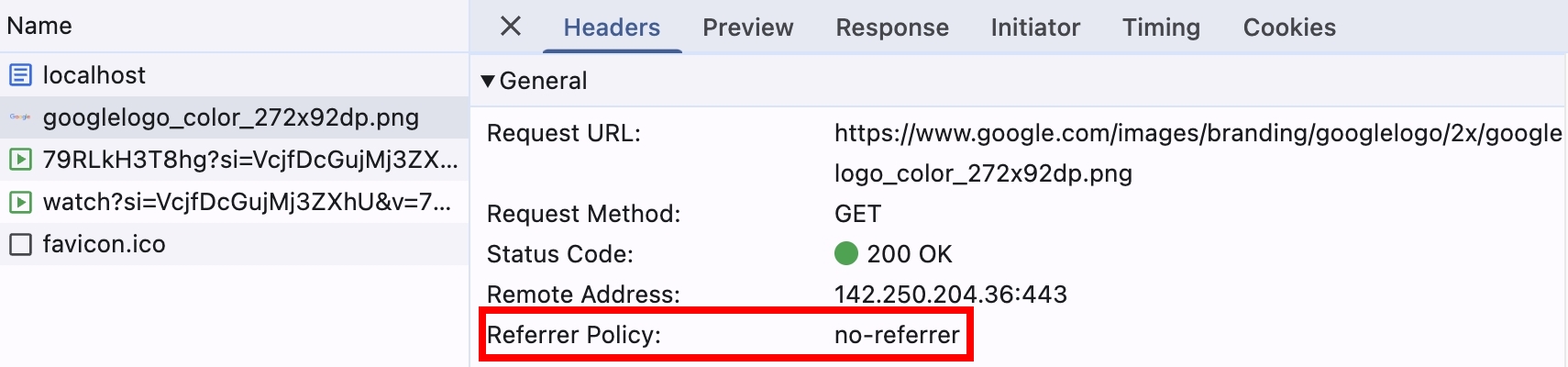
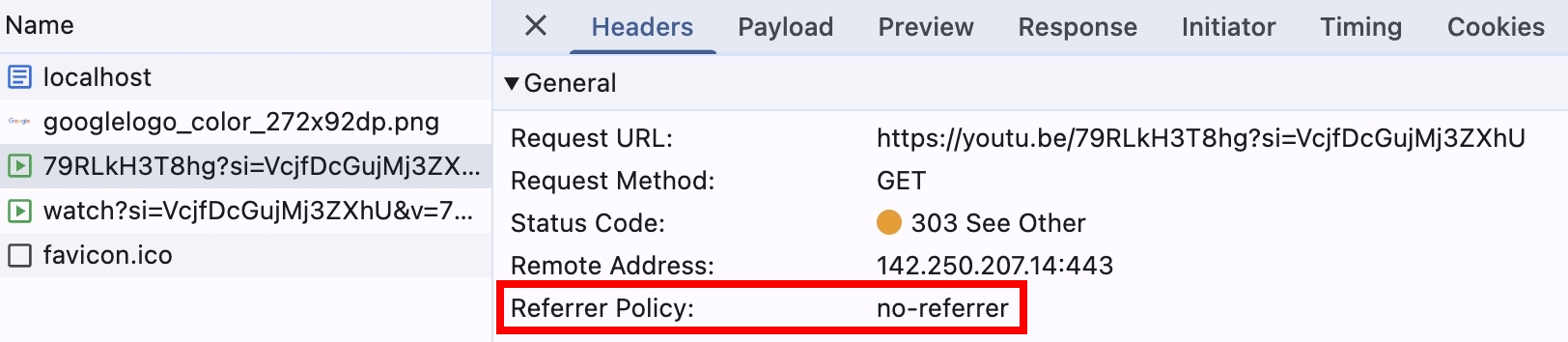
fetch API 是否也會套用 Response Header 設定的 referrerPolicy?
我們接著使用 fetch API,觀察 Referrer Policy 是否也變成 no-referrer
fetch("http://localhost:5000/");
fetch("http://localhost:5000/", { method: "POST" });
fetch("https://www.google.com/");
可以觀察到 General > Referrer Policy: no-referrer,我們可以得出一個結論,當 Response Header 有設定 Referrer Policy,就會覆寫瀏覽器的預設值
By Request 設定的 referrerPolicy,優先度會比較高嗎?
我們再繼續嘗試,如果在 fetch API 指定 referrerPolicy,這個優先級會高過 Response Header 設定的 Referrer Policy 嗎?
fetch("http://localhost:5000/", { referrerPolicy: "origin" });
fetch("http://localhost:5000/", { referrerPolicy: "origin", method: "POST" });
fetch("https://www.google.com/", { referrerPolicy: "origin" });
可以觀察到 Request Headers > referrer: http://localhost:5000/,我們可以得出一個結論,優先順序: By 請求設定的 > Response Header 設定的 > 瀏覽器的預設值
HTML 也能設定 referrerPolicy?
HTML meta 標籤可以設定全局的 referrerPolicy,作用就跟從 Response Header 設定是一樣的,我們調整一下 NodeJS 的程式碼:
httpServer.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.end(`<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="referrer" content="origin" />
</head>
<body>
<video src="https://youtu.be/79RLkH3T8hg?si=VcjfDcGujMj3ZXhU"></video>
<img src="https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png" />
</body>
</html>`);
});
可以看到請求圖片跟影片的 Request Headers 都有帶上 referrer: http://localhost:5000/ 了
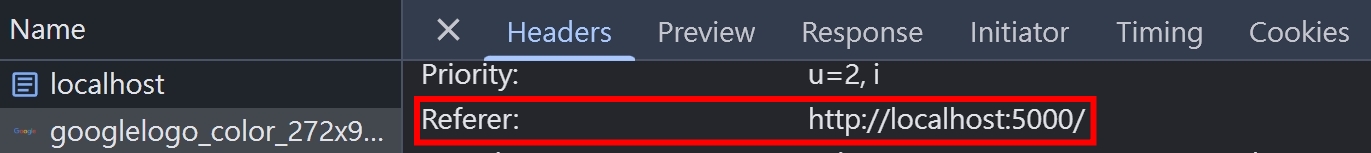
另外還有一些常見的 HTML 標籤也都可以 By 請求設定 referrerPolicy,例如 <a>, <img> 跟 <script>,我們試著在 NodeJS 加入以下程式碼,並且打開 http://localhost:5000/test/?a=1&b=2
httpServer.on('request', (req, res) => {
console.log(req.headers.referer);
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.end(`<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta name="referrer" content="origin" />
</head>
<body>
<a href="http://localhost:5000/" target="_blank" referrerpolicy="unsafe-url">google</a>
<a href="http://localhost:5000/" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer">google</a>
<img src="https://www.google.com/images/branding/googlelogo/2x/googlelogo_color_272x92dp.png" referrerpolicy="no-referrer" />
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@18/umd/react.development.js" referrerpolicy="no-referrer"></script>
</body>
</html>`);
});
點擊第一個超連結時,Server Log 預期會收到
http://localhost:5000/test/?a=1&b=2
http://localhost:5000/
第一個是 <a href="http://localhost:5000/" target="_blank" referrerpolicy="unsafe-url">google</a>
第二個是瀏覽器請求 favicon.ico 會吃到全局的 <meta name="referrer" content="origin" />
點擊第二個超連結時,Server Log 預期會收到
undefined
http://localhost:5000/
第一個是 <a href="http://localhost:5000/" target="_blank" rel="noreferrer">google</a>
第二個是瀏覽器請求 favicon.ico 會吃到全局的 <meta name="referrer" content="origin" />
<script> 跟 <img> 也都符合預期,沒有發送 referer
從 Google Map Embed API 來了解 referrer-policy 的實務應用
我們來創建一個 Google Map API Key
https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/javascript/get-api-key#create-api-keys
點擊按鈕 "Go to the Credentials page",如果你從來沒有玩過 Google Cloud Platform 的話,會需要先用 Google 帳號登入,然後綁定信用卡,但等等的範例不會真的收費。創建好之後,應該會拿到一組 AIzaSyBqM4KkMcP5x5x7xR8j2Y9nL3Q2xXxXxXx 的 Key
我們進到 Edit API Key 的頁面
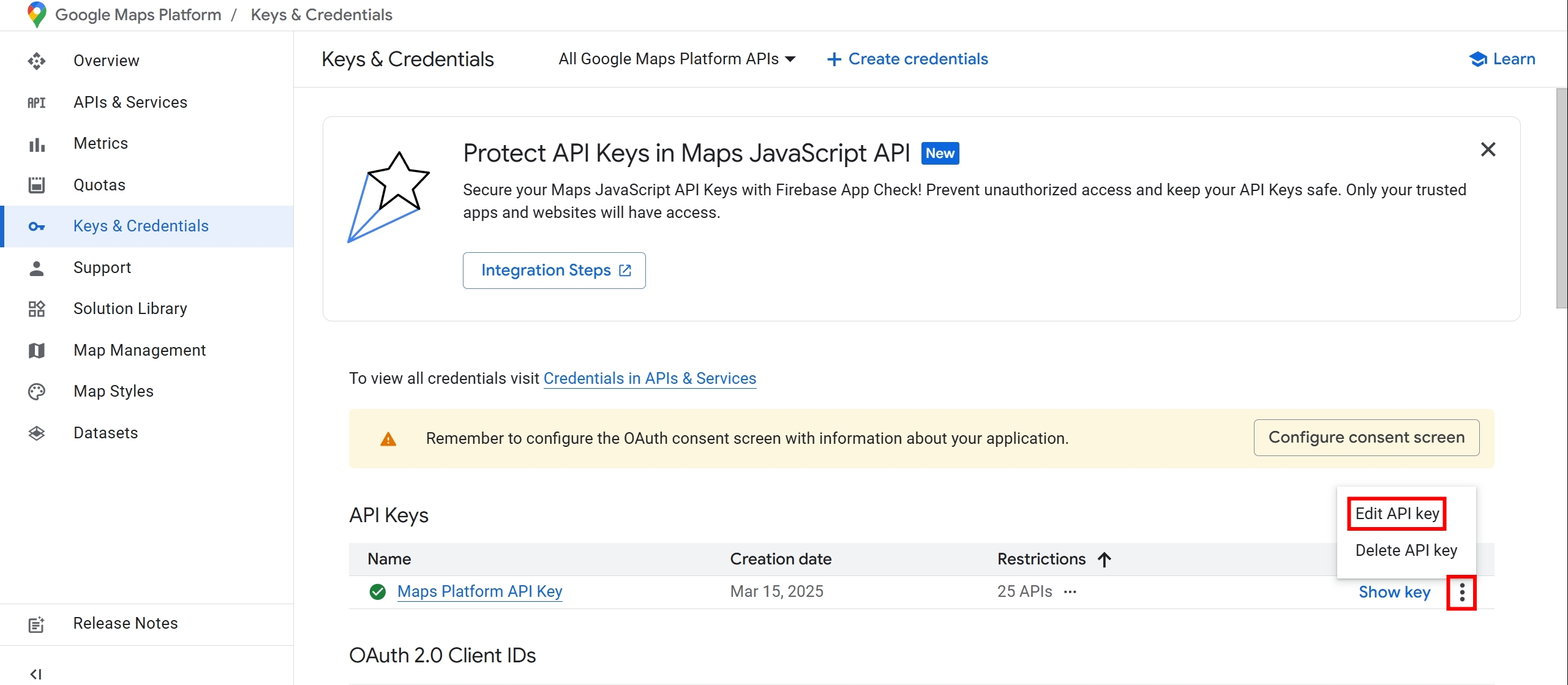
設定 Website restrictions,限制只有 http://localhost:5000 可以存取
https://developers.google.com/maps/documentation/embed/get-started
接著我們參考 Google Map Embed API 的官方文件,用 NodeJS HTTP Module 建立一個簡單的 HTML 頁面
import { createServer } from 'http';
const httpServer = createServer().listen(5000);
httpServer.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.end(`<iframe
width="600"
height="450"
style="border:0"
loading="lazy"
allowfullscreen
referrerpolicy="no-referrer-when-downgrade"
src="https://www.google.com/maps/embed/v1/place?key=API_KEY
&q=Taipei+101">
</iframe>`);
});
用瀏覽器打開 http://localhost:5000/ ,應該就會看到 Google Map 成功載入了
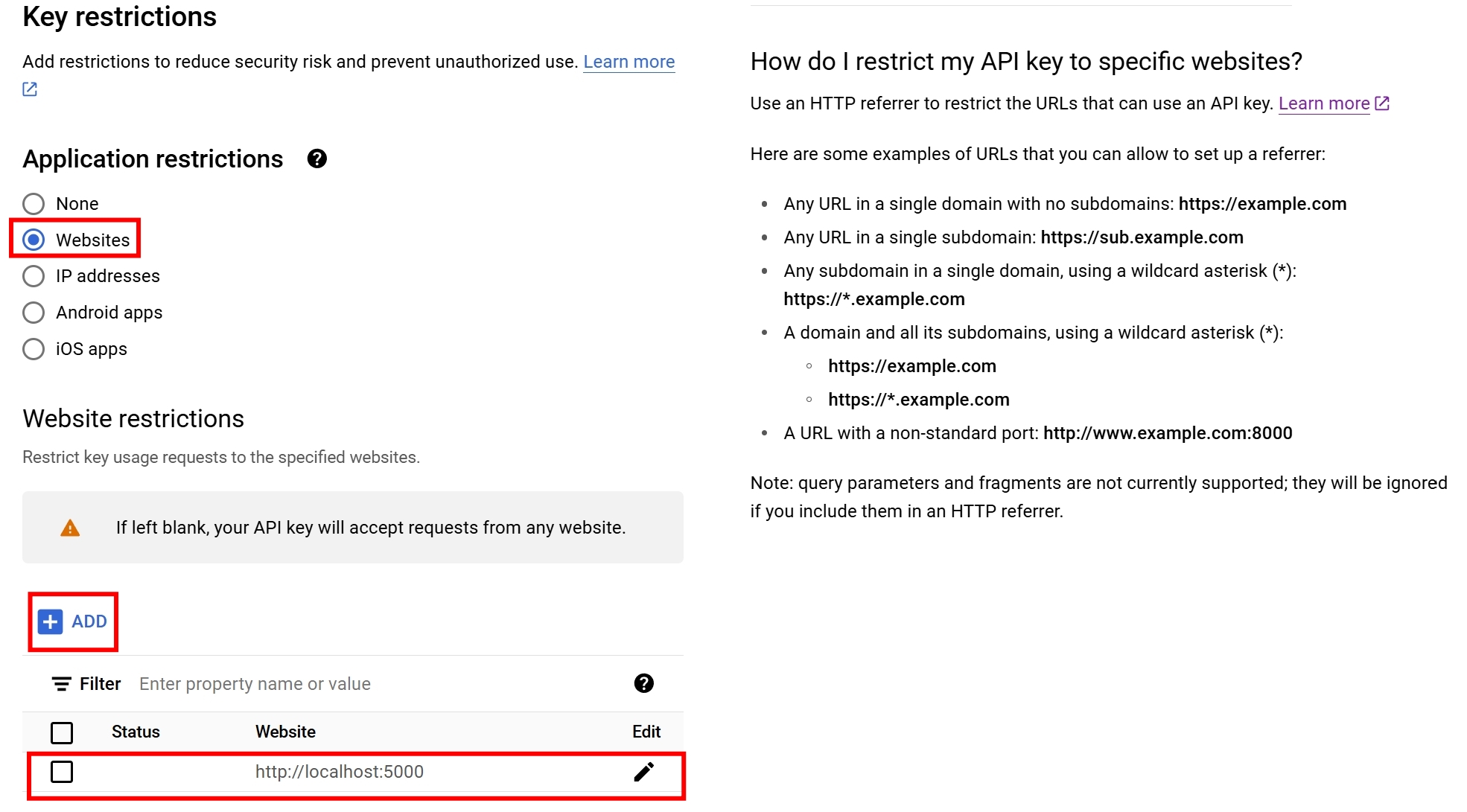
我們試試看把 Website restrictions 改成 https://www.google.com ,並且儲存
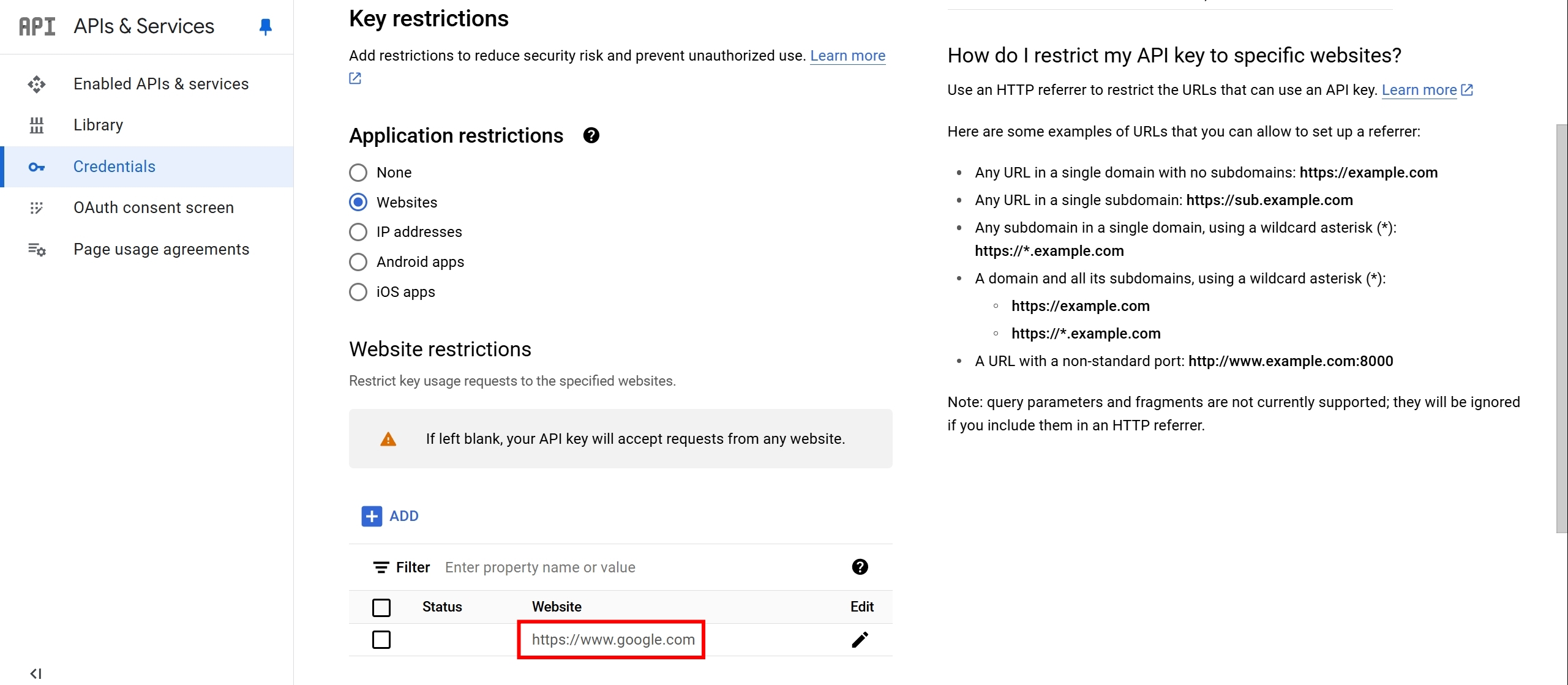
儲存後,再度重整 http://localhost:5000/ ,這時候應該就會看到以下錯誤訊息
Google Maps Platform rejected your request. This IP, site or mobile application is not authorized to use this API key. Request received from IP address x.xxx.xx.xxx, with referer: http://localhost:5000/
結合我們之前學到的 referrerPolicy,我們可以修改 <iframe referrerpolicy>
httpServer.on('request', (req, res) => {
res.setHeader("Content-Type", "text/html");
res.end(`<iframe
width="600"
height="450"
style="border:0"
loading="lazy"
allowfullscreen
referrerpolicy="no-referrer"
src="https://www.google.com/maps/embed/v1/place?key=API_KEY
&q=Taipei+101">
</iframe>`);
});
再度重整 http://localhost:5000/ ,就可以看到 Google Map 又順利載入了!
深入研究的話,還真的有人曾經回報這個問題給 google:
https://issuetracker.google.com/issues/366168659
但後來被標記為 Won't fix (Infeasible),我覺得也合理,我個人推測的原因如下:
-
每個網站設定的
referrerPolicy都不一樣,如果 Google 強行把判斷referer的規則變嚴格,會導致向後不兼容,依賴於 Google Map API 的網站就會壞掉 -
Website restrictions 本來就不是唯一限制 API Key 安全性的手段,還有 API restrictions, URL Signing Secret 等等,都可以保護 API Key
結論,多層的防禦總是比較安全,至少當前面幾層被攻破的時候,後面還有幾層可以保護!